The visible light spectrum is made up of a variety of wavelengths, for all different colors. Red, Green, Yellow… all the colors of the rainbow; including the dreaded blue light. But unlike the others, blue light wavelengths have more sinister characteristics.
What is the wavelength of blue light?
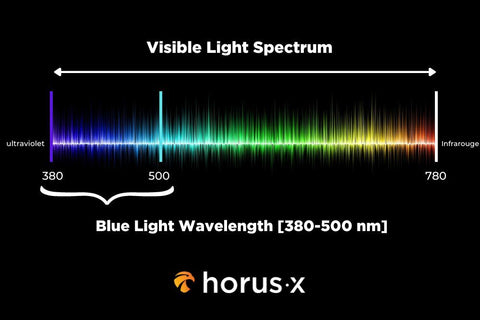
The visible light spectrum runs between 380 to 780 nanometers. The harmful blue light wavelength sits in this spectrum between 380 and 500 nanometers, just below green light and above UV light.
That means blue light is not represented by a single color, but all the shades between ultra-violet and green:
- Violet (up to 445 nm)
- Violet blue (up to 455 nm)
- Blue violet (up to 470 nm)
- Blue (up to 480 nm)
- Blue green (up to 485 nm)
- Green Blue (up to 500 nm)
Like Kevin Hart, these wavelengths are particularly short and intense in energy. The closer the color is to the UV part of the spectrum, the more intense and dangerous the light is.
Where does blue light come from?
☀️Sunshine
Unless you’re a vampire then you’ve definitely had a healthy dose of natural blue light from the sun. The light it emits is actually white light, which means it contains all the colors in the visible spectrum, including blue.
Don’t worry you’re not going to start sparkling like Edward, but it is important to be aware of this blue light, and remember it’s always there. That means in rain, or shine. It’s not just on sunny days when the sky is blue, you can also see the reflections of blue light when it rains, or when you see a rainbow.

💻 New technologies
The worst source of blue light exposure is all the screens and new tech we keep putting in our faces. There is no dark side of the moon when you’re constantly watching a digital screen; and they all emit artificial blue light. Whether it’s your phone, tablet, TV or LED lights in your home, they’re all sources of high energy blue light that will disrupt your sleeping patterns.
What are the dangers of the blue light wavelength?
The short wavelength of blue light is intense, which is the main reason it can pose a risk to humans… and maybe your dog if they really like TV.
Dangers of blue light include:
- 👁️ Computer vision syndrome or digital eye strain
- 💤Negative impact on sleep by reducing melatonin production
- 👴 Potential Age Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
- 🤪Attention deficit in children
- 📈 Acceleration of puberty
Studies on the effects of blue light exposure are still relatively new, but more and more ophthalmologists and other experts are warning people to be cautious. There’s a lot still to learn but the risks are getting more and more clear as the new digital age grows.
The most dangerous wavelengths by time of day:
- ☀️ During the day: between 380 to 450 nanometers.
- 🌙 Evening: 380 to 500 nanometers (full spectrum)
During the day, the shortest wavelengths impact the retina. But in the evening, any blue light exposure will impact the production of melatonin, the hormone that regulates your sleeping pattern. Therefore, any blue light in the evening will impact how well you doze off. Or maybe you just watched Smile right before bed…

How to protect yourself effectively from blue light
It’s both simple and complicated. Like trying to justify why you still listen to 90s pop.
Complicated because blue light is everywhere, and depending on the time of day it can actually be beneficial; which of course means no need to filter it out.
Simple, because the means to protect yourself are numerous and effective.
Here’s 3 easy ways to protect yourself from blue light wavelengths:
- Less screen time in the evening, especially before bed
- Use a blue light blocker/app for your devices where possible
- Wear effective blue light blocking glasses
Our recommendation on the best blue light glasses:
☀️During the day, if you’re spending a lot of time on your phone, tablet or a computer; you should check out Horus X’s Nomadic anti-blue light collection.
🌙In the evening when you’re binge watching Andor or trying to complete God of War Ragnarok in one night (not possible, by the way… put the controller down); you should jazz up your gaming set-up by adding a pair of glasses from our Gaming Glasses collection.

The blue light wavelength: Final thoughts
With a wavelength between 380 and 500 nanometers, blue light is super powerful and can seriously affect your eye health long term. With our technology heavy lifestyles, we’re under constant exposure, so good protection is crucial.
FAQs & community questions
How do you measure blue light?
To be exact, you’ll need a spectrometer. It’s a bit pricey and might not be necessary for the average person, but it is the only way to accurately and precisely measure blue light.
What is the blue light wavelength?
All blue light falls between the wavelengths of 380 to 500 nanometers.
What is the red light wavelength?
All red light falls between the wavelengths of 600 to 780 nanometers.
What are all the color wavelengths?
- 🔵Blue light: 380 - 500 nanometers
- 🟢Green light: 500 - 570 nanometers
- 🟡Yellow light: 570 - 590 nanometers
- 🔴Red light: 590 - 780 nanometers
Important note: The actual limits and ranges can vary, some studies report change quite drastically. That means these are all approximate as each spectrum merges into the next.
Where can you find blue light?
🎶It’s written on the wind; it’s everywhere I go…
In all seriousness, blue light really is everywhere. It’s in the light emitted by the sun, and all your LED lights and digital screens.
Blue light poses a real risk: True or false?
It’s unfortunately true! Blue light is both a natural and artificial phenomenon that has a strong impact on the body. It’s both necessary for our natural circadian rhythm, and dangerous, because too much impacts our eye health and disturbs our sleeping patterns.















